CCTV News: trillions of microorganisms are inhabited by the human intestines. In addition to assisting in digesting food, some specific bacteria also play a key role in shaping the immune system. In such a complex microbial community, how does the human body accurately identify useful specific bacteria and resist invasion of harmful pathogens at the same time? Recently, Chinese scientists have successfully solved this problem, revealing the new mechanism of host identification of intestinal bacterial flora to regulate immunity, and found proteins that help enhance intestinal immune defense. This result was published in the international academic journal Nature on May 14.

Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the team of the Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences found that a protein called APOL9 can establish refined cooperation with specific bacteria to help maintain intestinal immune homeostasis. This protein can accurately identify a class of Bacteroidetes symbiotic bacteria, but after identification, it will not directly kill bacteria, but induce bacteria to release signals to "talk" with the body, helping to trigger a beneficial immune response, thereby significantly improving the intestinal defense ability against harmful bacteria. This study reveals a new mechanism for intestinal bacterial flora to regulate immunity, deciphers the molecular code, and will open up new paths for the treatment of human intestinal diseases.
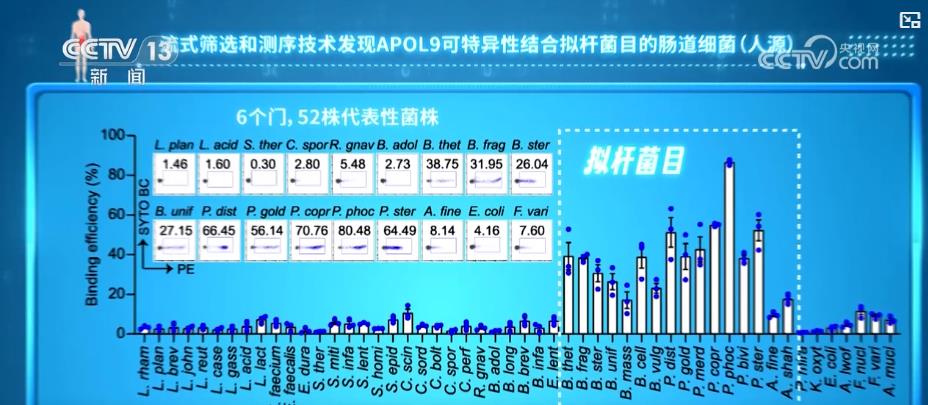
Associate Researcher Yang Tao, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Although our research this time is relatively cutting-edge and basic, it has also opened up ideas for future practical applications. This mechanism can be used to develop new drugs, such as activate certain beneficial bacteria, and help regulate the human immune system or metabolism. In addition, it may even be possible to design new oral vaccines or intestinal treatments based on this discovery in the future to combat some diseases related to intestinal flora disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune diseases, or metabolic diseases.